Table of Contents
It is very common for people to undergo “health screening”. A health screening is basically a package of tests that are carried out to try and pick up diseases at an early stage. If you find a disease early, then it can potentially be treated before it goes on to cause symptoms and more serious problems.
A big part of screening is to pick up early signs of heart and vascular disease (atherosclerosis). Heart attack and stroke (cardiovascular disease) are the leading cause of death globally, taking an estimated 18million lives per year. If you can prevent it developing or catch it at an early stage, then you can prevent people dying.
What is the purpose of heart screening?
In general heart screening is looking for 2 things:
- The presence of risk factors for cardiovascular disease such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol
- Evidence of any current heart disease.
This is done using blood tests, stress tests and different imaging tests of the heart and arteries.
Who needs heart screening? What does the Ministry of Health in Singapore recommend?
Blood pressure: If you are over 40 you should have your blood pressure checked at least once per year.
Cholesterol: Should be checked if you fit any of the following criteria:
- Over 40
- Previously had a heart attack or stroke
- Have a history of diabetes
- Have family with high cholesterol
You should also get your cholesterol checked if you are over 30 and have other risk factors for heart disease like smoking, high blood pressure, have family with heart disease before the age of 65 or you are Indian.
Obesity: All patients over the age of 18 years should be screened once per year.
Diabetes: Screening for diabetes should begin at 40 years of age, unless you have other risk factors like high blood pressure or are overweight, then it should begin much earlier. It is done with a simple blood test.
What do they do at a heart screening?
What gets done at your heart screening very much depends on the package you go for. Packages can be as simple as blood tests and a consult with a doctor in Singapore or can be more comprehensive (and more expensive…) and include CT scans and MRIs.
At a minimum, the following should happen:
- Consultation – Your cardiologist will ask you about any symptoms you have; your previous medical history; medications you are taking; your family history; and your smoking and alcohol history.
- Examination – Your cardiologist will look for signs of heart and vascular disease like eye changes, heart murmurs, change in breath sounds, swelling of the legs and the characteristics of your arterial pulses.
- Cholesterol check – A simple blood test to look at the levels of different types of cholesterol in your blood stream. It needs to be done when fasting for 10-12 hours to ensure the triglycerides are measured correctly.
- Blood pressure check –Ideally this is something that you can do yourself at home too with a home blood pressure monitor.
- Diabetes check – A simple blood test, done after fasting for 10-12 hours. It checks your blood glucose and your HbA1c (a blood test that looks at long-term blood glucose levels).
- Obesity screen –Your weight and height are measured, and your Body Mass Index (BMI) is calculated.
Most heart screening packages contain a lot more than the simple tests described above. Other blood tests and imaging tests are used to look at specific aspects of the heart and blood vessels and these are detailed below.
What are the different types of heart screening tests and why are they done?
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG)
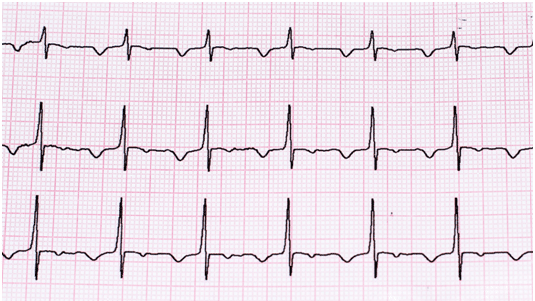
This is a simple test that records the electrical activity of the heart. It is good for assessing problems with the heart rhythm. In addition, it is used by your cardiologist to look for clues about the heart structure and function, if you have had a heart attack before or if you have signs of heart blockages, pericarditis or myocarditis. When you have the test done, you lie on a couch and small sensors are applied to your limbs and chest. It is very quick and painless.
Echocardiogram
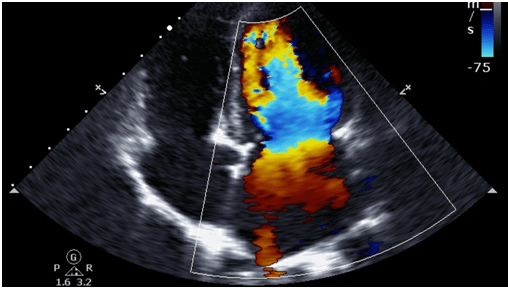
An “echo” is a heart ultrasound. It allows your cardiologist to examine the heart in detail: the pump function of the heart; thickness of the heart muscle; and heart valve function. It is especially useful for picking up signs of previous heart attacks, heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathies) and for assessing causes of breathlessness.
The test is non-invasive, and uses high frequency sound waves to build detailed pictures of the heart. There is no radiation involved and it only takes about 30 minutes to perform.
Stress tests
Cardiac stress tests are used to measure how the heart responds to stress. The signs and symptoms of coronary artery disease (blockages) often only appear at times when the heart is put under stress. This is because at rest the heart does not need a lot of blood supply so even if there is a blockage in a heart artery, the heart muscle still gets enough blood. On exercise, the heart muscle needs a lot more blood to get down the coronary artery, and if you have a significant blockage then the heart muscle will not get enough blood at times of exertion. The stress test is designed to pick up when the heart muscle is not getting enough blood either through changes in the ECG, echo or nuclear scan.

- Treadmill ECG – This is also known as an exercise tolerance test. You have ECG leads fitted and then are asked to walk on a treadmill. The treadmill gradually gets faster and steeper, slowly increasing the workload and stress on the heart. The ECG indicates if there are any blockages in the heart arteries.
- Stress echocardiography – The same process as for the treadmill ECG, but an echocardiogram is performed at rest and at peak exercise. This allows your cardiologist to look at the way the heart moves during exercise. It is more accurate than a plain treadmill ECG.
- Nuclear stress tests – Your doctor stresses you with a treadmill/bicycle or they use medication to “stress” the heart. You are also injected with a special radioactive tracer that allows your cardiologist to assess what areas of the heart have good blood flow. An X-ray camera is used to look at the heart and the blood flow.
CT calcium score
This is a simple, quick non-invasive test that uses a powerful CT scanner to calculate the amount of calcium in the heart arteries. The report gives you a coronary artery calcium score. The higher the score the greater the chance you have significant coronary artery disease and the higher your risk of heart attack. There is no injection needed. It does not give any information on the severity of blockages, but it provides excellent information that is used to predict your future risk of heart attacks and coronary artery disease.
Carotid or femoral doppler ultrasound
This is an ultrasound assessment of the arteries in the neck (carotid) and the arteries in the top of the leg (femoral). It allows the health of the arteries to be directly visualized. At the neck we can measure CIMT (Carotid Intima Medial Thickness) as a measure of cardiac risk. The thicker the walls, the higher your risk of heart attack and stroke. It also allows us to directly visualize if you have any arterial disease in the walls (plaques).
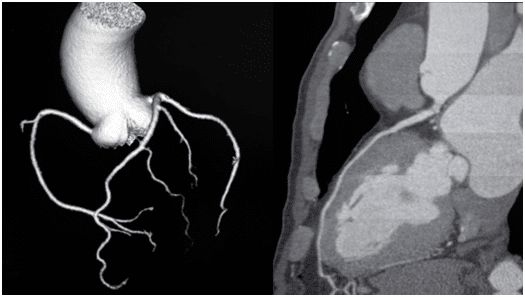
CT coronary angiography (CTCA)
This is a non-invasive assessment of the heart and the heart arteries using a powerful X-ray CT scanner. It gives very detailed still pictures of the coronary arteries and if there are any blockages present. The test takes around 30 minutes and requires an injection of iodine-based contrast. It is very low risk overall.
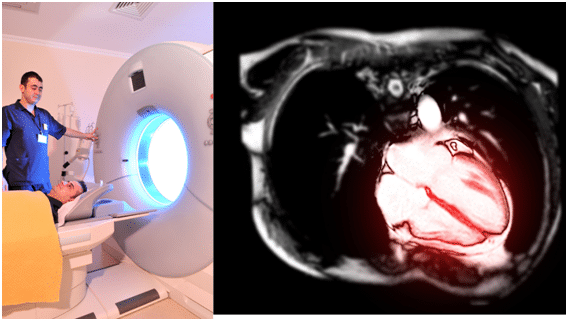
Cardiac MRI
This is an advanced assessment of the heart structures using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This is a special technique that uses a very powerful magnet to take images. It does not use any X-rays/radiation. It is the gold standard technique for assessing heart function.
Using a special contrast agent called Gadolinium can also pick up the previous scarring in the heart muscle and is the most sensitive technique for picking up previous myocardial infarctions (heart attacks). Interestingly if you do a cardiac MRI scan in diabetic patients around 20-30% will have evidence of a heart attack that they did not even know about! Only a few doctors can do this type of imaging. Dr MacDonald is highly qualified to perform and interpret cardiac MRIs.
Invasive coronary angiogram
This is an invasive test to assess the heart arteries for blockages. A thin tube is inserted into the arteries at the wrist or the top of the leg and this is pushed up to the heart and positioned in the coronary arteries. Iodine-based contrast is then injected into the coronary arteries and X-ray pictures are taken to identify any blockages. This is an invasive test so there is a small risk of heart attacks and strokes with the procedure. It is therefore only done if necessary, ie if a stress test or cardiac CT show significant blockages.
MRI Brain – A brain MRI scan can be done to look for evidence of vascular disease and strokes. Sometimes people can have strokes and small vessel disease that they did not know they had.
What test shows a heart blockage?
Blockages can be assessed using a stress test which looks at the consequences of a severe blockage, or an anatomical test like CTCA or invasive coronary angiogram.
What are the warning signs?
Possible warning signs of a heart problem can be chest pain/discomfort; shortness of breath; palpitations; syncope; giddiness; high blood pressure.
What happens at a heart screening consultation?
Your consultation will start with a structured discussion “history taking” where your cardiologist will discuss your symptoms, family history, past medical history, smoking and alcohol history etc. It will then be followed by an examination focusing on the heart and vascular system and then a discussion about what tests you should consider having.
How should blood pressure be taken?
Blood pressure should be taken when you are sitting and relaxed. Never take it when stressed or rushing. You should sit comfortably for 5 minutes before taking your blood pressure with your arm supported.
Why is family history important?
Family history of heart disease is incredibly important, particularly if there is a history of heart disease in members of your family before the age of 65. It gives a clue as to genetic conditions that can predispose to heart problems like genetically high cholesterol – familial hyperlipidemia.
What are all the components of the cholesterol test?
Cholesterol is a waxy fatty substance (lipid) that is made by the body and is essential for many functions in the body. For example, cholesterol is used to make the cell membrane that surrounds every cell in the body and it is also used to make some hormones. It is a fat so is not soluble in water. To transport it around the body the fats (lipids) are packaged with proteins (lipoproteins). The components in a standard cholesterol test measure the amount of cholesterol in different types of lipoproteins.
- Low Density Lipoprotein (“bad cholesterol”) – Higher levels of this type of cholesterol are associated with atherosclerosis (fatty plaques in the artery walls) and consequentlyheart attacks and strokes.
- High Density Lipoprotein (“good cholesterol”) – This type of lipoprotein carried fats away from the artery wall and higher levels of HDL are associated with lower risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Triglycerides – These enter the blood stream after a meal and are used for energy or to store fat for later.
Cholesterol components and types are a little more complicated than this, but as a rule the most important factor in your blood test is LDL. The lower your LDL is the lower your risk of heart attack and stroke.
The following cholesterol lab tests are more specialized but give you extra information on your risk:
- Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) – is a structural protein that attaches to the LDL particle. Each LDL particle has one ApoB molecule on it so when you assess ApoB levels it corresponds to the total number of LDL particles. It is the particle count that is more associated with atherosclerosis than the total cholesterol within the LDL particles (which is measured in the standard tests). You can check how you compare with other people in the population using this calculator.
- Lipoprotein (a) – This is an LDL particle with an additional protein attached to it called apo(a). An individual’s level is genetically determined, some people don’t make it at all. High levels of Lp(a) are associated with early cardiovascular disease and valvular heart disease. Everyone should have it checked at least once in their life.
What other blood tests can be done to assess heart and vascular risk?
- NTproBNP (Brain Natriuretic Peptides) – This is a protein that is made by your heart and blood vessels. If your heart is damaged and failing to do its job properly it tends to make more of this protein. A simple blood test can determine your level and help diagnose heart failure.
- High sensitivity CRP (hsCRP) – C Reactive Protein (CRP) is a protein that is made by your liver in response to inflammation and infection. It can be measured in a simple blood test and higher levels of hsCRP are associated with higher risk of heart attack, stroke and cardiovascular disease.
- Troponin – This is a protein found in heart muscle. If you have high levels of troponin in your blood it suggests you have some heart muscle disease or have had a recent heart attacks.
What does your cardiologist do with all the information obtained during the screening?
Your cardiologist will take all the information and work out your risk of developing cardiovascular disease or if you already have cardiovascular disease. They will be able to determine what your key risk factors are and what you can do to lower your risk. This may be lifestyle adjustments like stopping smoking or it could involve medication or a procedure. They will discuss all the options with you at the end.
Dr Michael MacDonald is an expert in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease. If you would like to arrange a consultation or discuss what you can expect on your heart screening in Singapore as well as find out what tests are most appropriate for you, then just get in touch at mmichael.macdonald@harleystreet.sg.
Related article: 6 Ways to Lower Your Cholesterol Naturally

