Contents
- 1 Heart Procedures
- 1.1 Coronary Angiography.
- 1.2 Percutaneous Coronary Angioplasty and Stenting.
- 1.3 IVUS & Pressure Wire Study.
- 1.4 Permanent Pacemaker (PPM) Insertion.
- 1.5 Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD) Insertion.
- 1.6 Implantable Loop Recorder (ILR) Insertion.
- 1.7 Right Heart Catheter Study.
- 1.8 Cardiac Rehab.
- 1.9 PPM, ICD, and ILR Checks & Follow-up.
- 1.10 Remote Home Monitoring of Implantable Cardiac Devices.
- 1.11 Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery.
- 1.12 Valve Replacement and Repair.
- 1.13 Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI).
- 1.14 Aneurysm Repair.
Heart Procedures
With our state-of-the-art technology and highly-skilled clinicians and heart doctor in Singapore, we offer the following diagnostic and interventional procedures, some in conjunction with other specialists like cardiac surgeons.
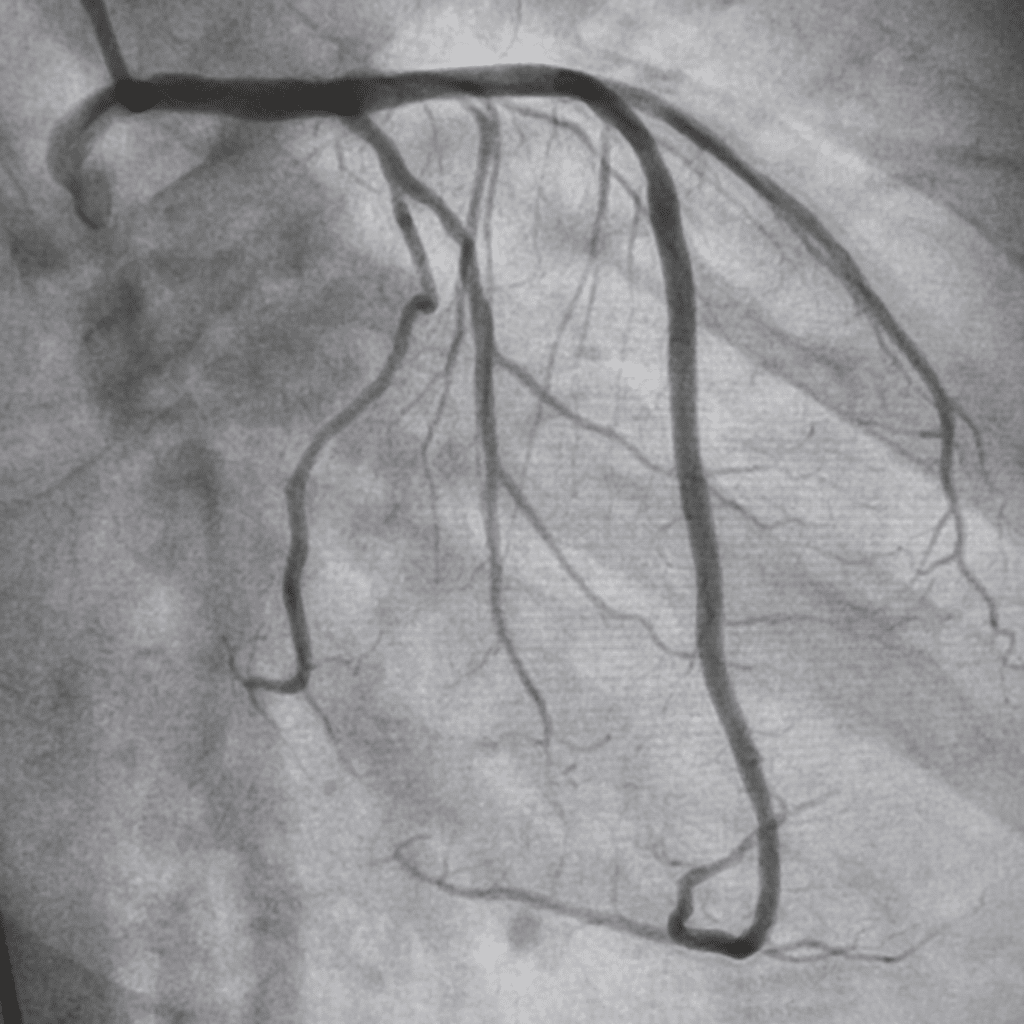
Coronary Angiography.
Coronary angiography is a minimally invasive procedure performed under local anesthesia. It is a diagnostic test that examines the heart and its adjacent blood vessels using X-ray and contrasting dye containing iodine. A catheter is inserted through the arm or groin to take pictures and identifies blockages in the coronary arteries.
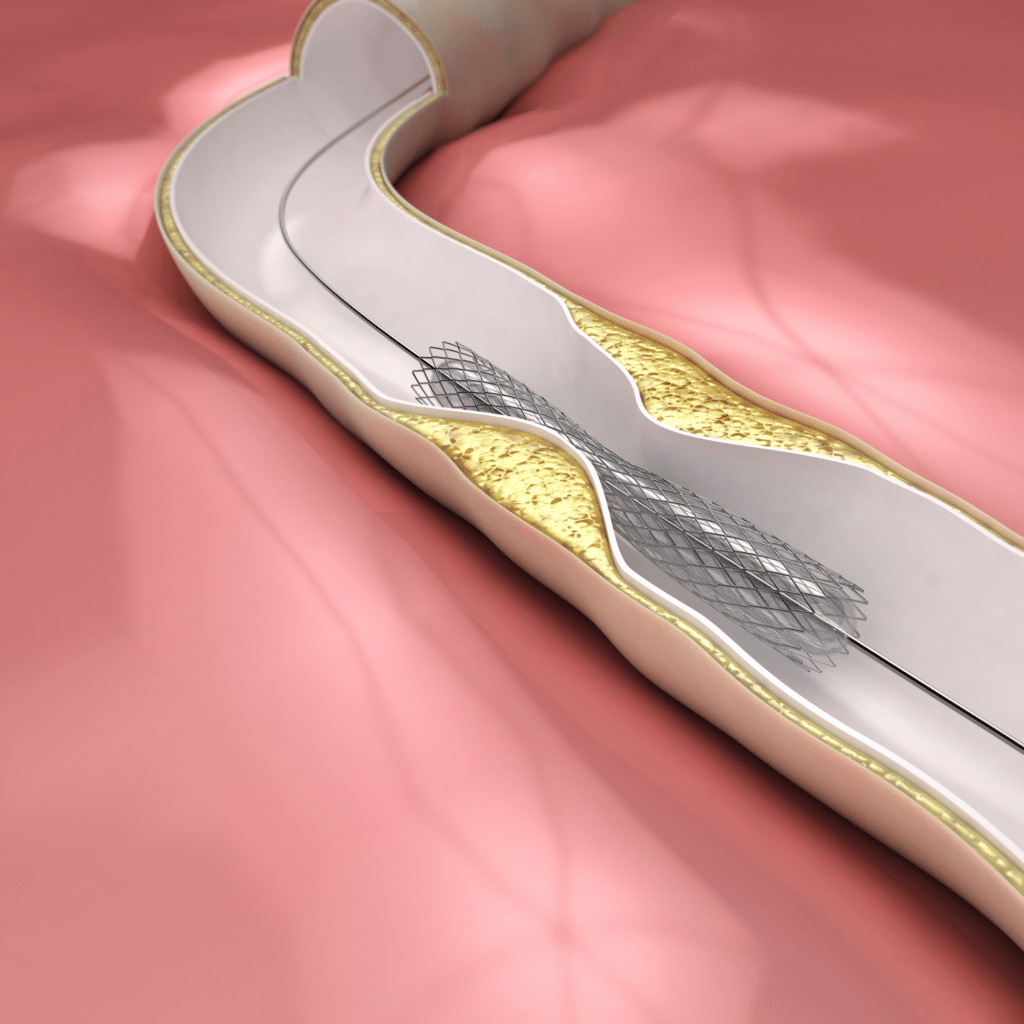
Percutaneous Coronary Angioplasty and Stenting.
Percutaneous coronary angioplasty is an interventional cardiology procedure that aims to dilate a narrowing coronary artery. Done under sedation or local anesthesia, this involves an initial coronary angiogram to look at the blockages. A guidewire is then inserted, followed by a tiny balloon that is dilated in the blocked blood vessel, thus improving the blood flow to the heart. A small metal stent is often left in place to hold the artery open.
IVUS & Pressure Wire Study.
Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) is an ultrasound-guided procedure that checks the interior of coronary blood vessels to assess blockages. A pressure wire is an invasive technique that may be used when the degree of stenosis is marginal. Both can be done at the time of coronary angiography.
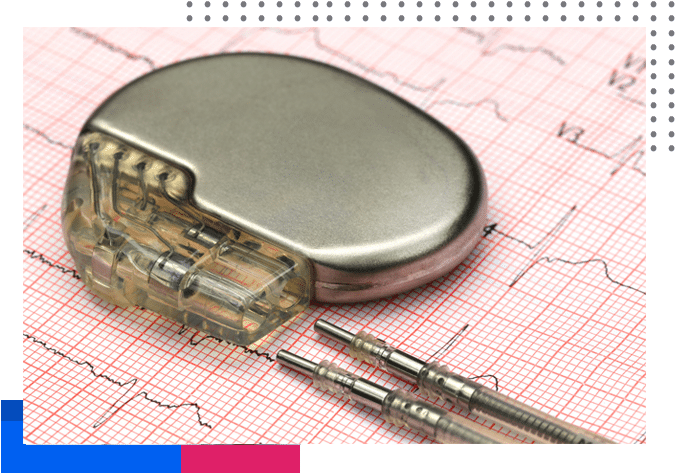
Permanent Pacemaker (PPM) Insertion.
A pacemaker is an artificial device that helps the heart transmit a natural heart rhythm and electrical pulses. It can be temporary or permanent.A permanent pacemaker is indicated for people with chronic heart rhythm problems, such as cardiomyopathy, tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome, and atrial fibrillation with sinus node dysfunction. Done under local anesthesia, a pacemaker device is usually fitted on the left side of the chest, and the wires are inserted into a vein leading to the heart.
Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD) Insertion.
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator is a battery-operated device placed underneath the chest to detect and treat irregular heartbeats. ICD works by delivering shocks to the heart if it detects an abnormal heart rhythm. It is the primary therapy in preventing sudden cardiac death from repeated heart attacks, ventricular arrhythmia, and congenital heart disease.
Implantable Loop Recorder (ILR) Insertion.
Implantable Loop Recorder (ILR) is a tiny needless box fixed underneath the skin. ILR is a type of ambulatory electrocardiogram (ECG) that records heart rhythm and activity up to three (3) years. It is the monitoring of choice for people who display very irregular and sporadic clinical manifestations, such as palpitations and syncope.
Right Heart Catheter Study.
A right heart catheter study is a day-case procedure that measures the pressure in the heart and lungs. It is performed by inserting a catheter into the large vein and up to the right side of the heart, where pulmonary pressures are taken and recorded.
Cardiac Rehab.
The goals of cardiac rehabilitation are to improve heart function and reduce risks. Cardiac rehab involves a comprehensive, systematic plan that focuses on enhancing cardiovascular health through exercise, education, counseling, behavior change, and lifestyle modification. It is an individualized program depending on the person’s health status, health goals, and teams involved.
PPM, ICD, and ILR Checks & Follow-up.
We carry out checks for different cardiac rhythm devices such as a permanent pacemaker (PPM), Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD), and Implantable Loop Recorder (ILR). Implanted cardiac devices should be checked regularly by a cardiologist to make sure that the device is functioning optimally and to ensure that reported subjective symptoms are expected and normal. The number of checks and follow-ups depends on the type of cardiac device and patient symptoms.
Remote Home Monitoring of Implantable Cardiac Devices.
We carry out checks for different cardiac rhythm devices such as a permanent pacemaker (PPM), Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD), and ImplantablPeople with implantable cardiac devices can now be reviewed by doctors and specialists remotely. Remote monitoring does not only save healthcare costs and resource utilization. But essentially, it provides substantial benefits in improving patient outcomes and reducing the mortality rate.
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery.
CABG is a treatment of choice for people with advanced-stage coronary artery disease (CAD). Also called bypass surgery, CABG involves the use of a healthy blood vessel and grafting it to the diseased coronary artery.
Valve Replacement and Repair.
Heart valves are flaps that keep one-way blood flow and prevent blood from regurgitating (or flowing back). However, valves can be affected by a disease or worn out over time. Either getting leaky or narrowed. Valve replacement and repair helps maintain correct blood flow direction.
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI).
TAVI is a minimally invasive procedure for aortic stenosis or the severe narrowing of the aortic valve. When not treated, symptomatic, severe aortic stenosis can lead to death.
Aneurysm Repair.
An aneurysm is the abnormal enlargement of an artery as a result of the accumulation of plaque or weakened interior wall. Aneurysm repair can be open surgery or endovascular approach depending on the position of the aneurysm and the patient’s health status. In aortic aneurysm repair, the plaque is removed, and a special graft is placed to support that section of the aorta.

